During Green Careers Week 2023 #GCW2023 we put out a number of Tweets and other content on social media about how Data Protection can be a Green Career. This article brings all of those ideas into one place… 🌍

Green Careers Week illuminates a vital truth: every profession, including data protection, plays a crucial role in shaping a sustainable future. As we navigate the digital era, the intersection of data protection and environmental stewardship becomes increasingly prominent.
Green Careers Week is not just about celebrating ‘green’ jobs in the traditional sense; it’s about recognising and enhancing the green potential within all career paths. For data protection professionals, this means redefining their role, extending beyond advice on compliance with the UK GDPR to also include fostering eco-friendly practices in data management. This pivotal juncture where data protection meets environmental responsibility marks a new frontier in our journey towards sustainability.
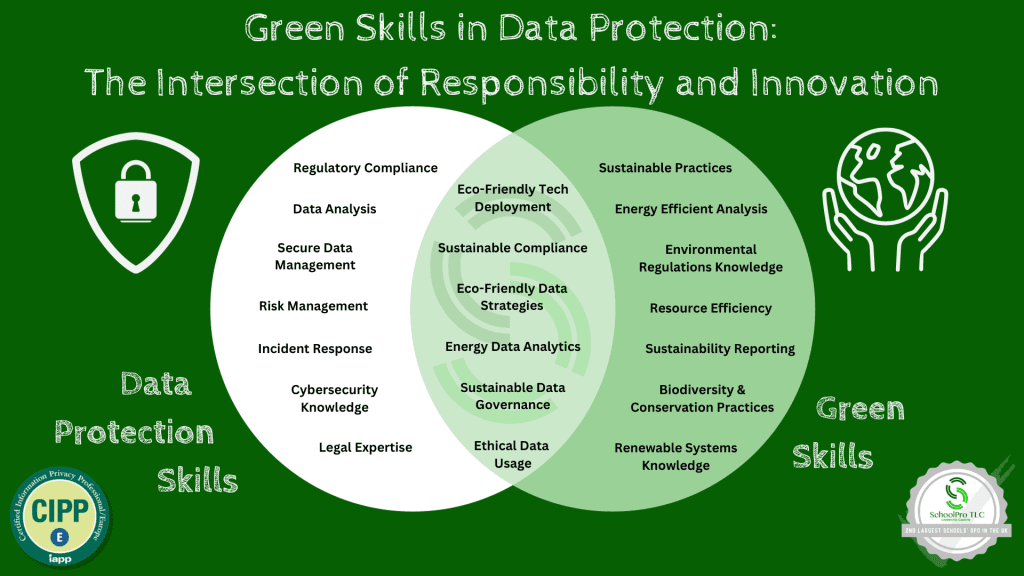
Green Skills in Data Protection
In the evolving landscape of data protection, ‘green skills’ are becoming increasingly vital. These skills blend environmental awareness with technical expertise, equipping professionals to support sustainability initiatives effectively.
Key green skills in data protection include:
🌍 Implementing eco-friendly data storage and processing methods.
🌍 Developing strategies for minimal and sustainable data usage.
🌍 Analyzing energy usage data to identify efficiency improvements.
🌍 Promoting sustainable governance and compliance.
🌍 Understanding and applying regulations that pertain to both data protection and environmental standards.
By mastering these skills, data protection officers can play a pivotal role in driving environmental initiatives within their organizations. Let’s explore ideas around data protection in green careers in more detail:
Data Protection as a Green Career
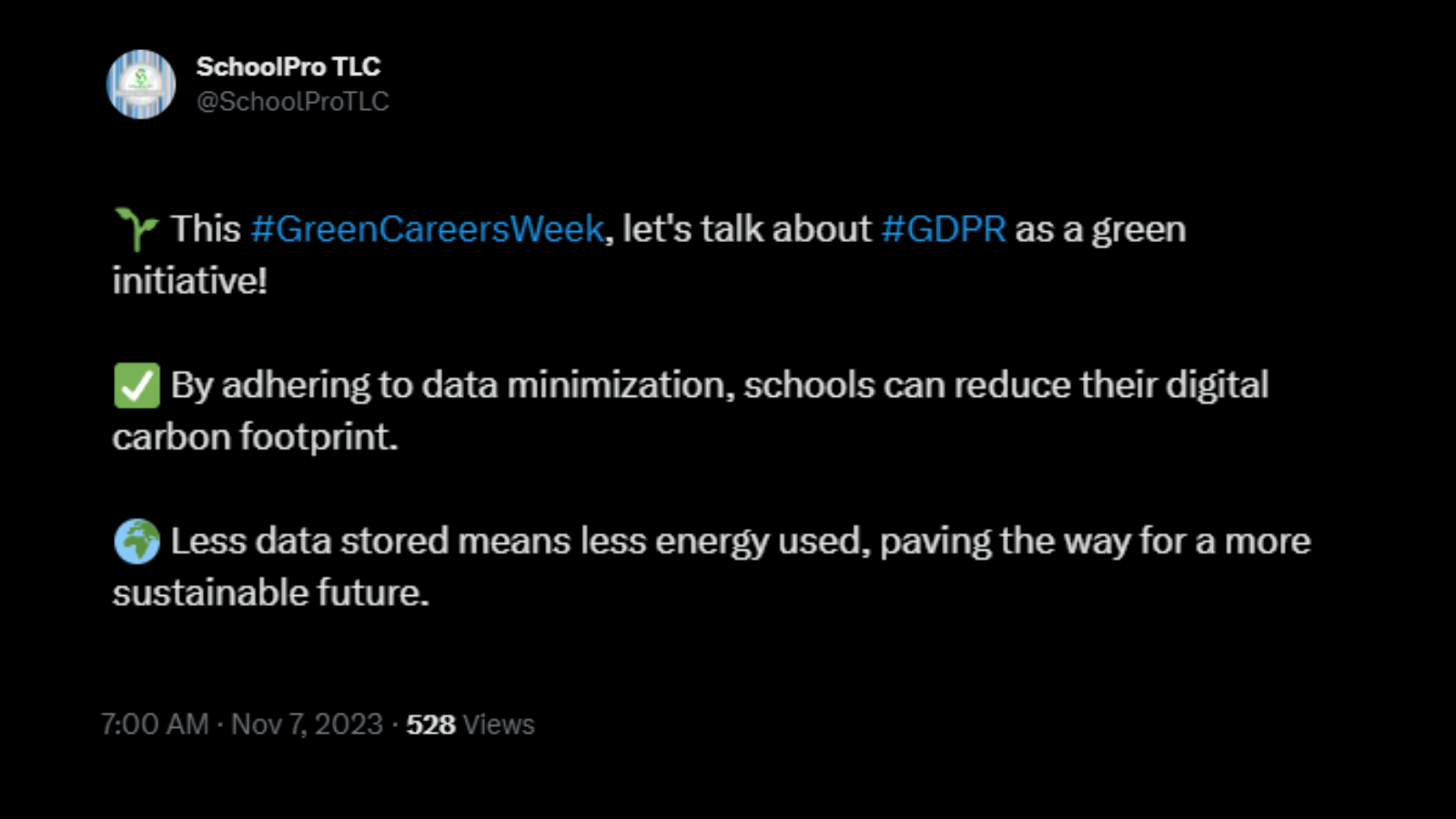
Data protection roles are increasingly recognised as integral to environmental sustainability. This alignment is most evident in the implementation of GDPR’s data minimisation principle. By mandating that personal data collection be “adequate, relevant, and limited to what is necessary,” GDPR inadvertently steers organisations towards greener practices. Less data collected means less storage required, leading to reduced energy consumption in data centres.
This principle not only protects personal data but also encourages a more efficient and environmentally conscious approach to data management. As such, data protection professionals find themselves as key players in reducing the digital carbon footprint, turning data management into an unexpectedly green career path.
Sustainable Practices in Data Centres and Cloud Computing
The evolution towards energy-efficient data centres and the adoption of cloud computing are pivotal in reducing the environmental impact of digital operations. Data centres, traditionally significant energy consumers, are increasingly transitioning to renewable energy sources and adopting advanced cooling technologies to reduce their carbon footprint.
Cloud computing offers a more energy-efficient alternative to traditional on-premises data centres. With cloud providers optimizing server utilisation and energy use, organisations can significantly lower their environmental impact. Additionally, advancements in data hardware, like the shift from SATA to NVMe and the use of SSDs, enhance performance while consuming less energy, further contributing to sustainability.


Eco-Friendly Data Destruction
Eco-friendly data destruction is an essential component of sustainable data management. Securely disposing of data not only ensures compliance with data protection regulations but also plays a significant role in environmental conservation. Proper methods for data destruction prevent sensitive information from falling into the wrong hands and support the responsible recycling of electronic waste.
This approach minimises the environmental impact of discarded electronic devices, which are a major source of pollution and resource depletion. By integrating eco-friendly data destruction practices, organisations can protect both their data and the environment.
Paper Reduction in Schools
The digital transformation in schools significantly contributes to reducing paper usage, offering dual benefits in data protection and environmental sustainability. Shifting from paper-based to digital records not only minimises the risk of physical data breaches but also reduces paper waste, directly impacting environmental conservation.
This transition towards digital documentation aligns with sustainable practices, fostering a culture of eco-consciousness in educational settings. By embracing digital methods, schools can efficiently manage data while actively participating in environmental stewardship.

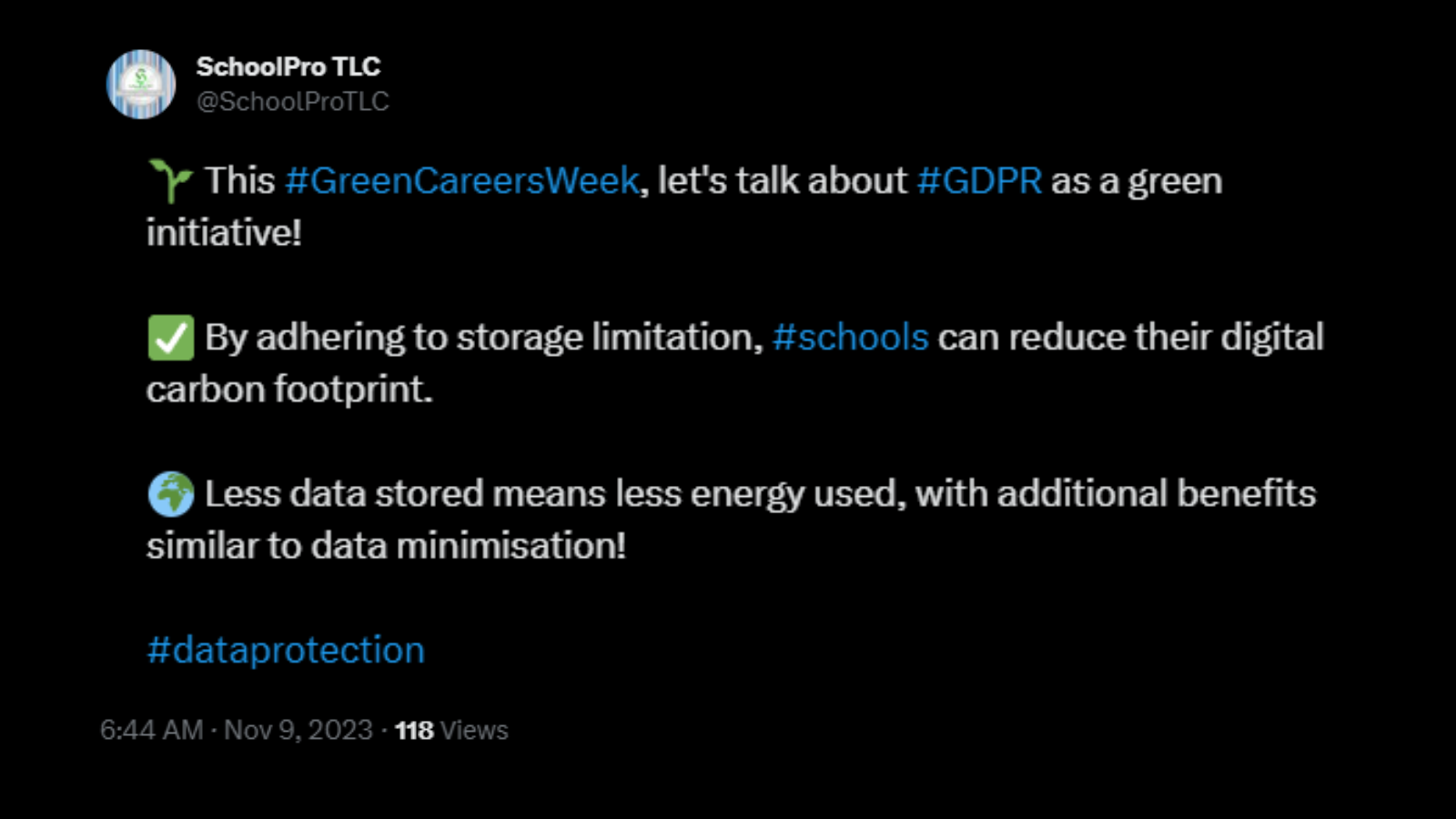
Storage Limitation Principle
Another useful tool in reducing the energy costs of data storage and processing is the Storage Limitation Principle of the UK GDPR. This principle calls for data to be kept “for no longer than is necessary for the purposes for which the personal data are processed,” encouraging businesses to retain data in an identifiable form for as short a time as necessary.
Much like the Data Minimisation Principle, this approach not only cuts costs but also reduces energy usage by eliminating unnecessary data storage and processing.
Conclusion
By embracing green practices within data protection roles, we can not only safeguard sensitive information but also contribute to a sustainable future. By integrating principles like the UK GDPR’s data minimisation and storage limitation, adopting energy-efficient data centres and cloud computing, practicing eco-friendly data destruction, and reducing paper use, data protection becomes a vital ally in environmental stewardship.
Let’s work to merge data protection with sustainability, forging a path where technological advancement and ecological responsibility coexist.
If you have any other questions about this or any other data protection topic, please contact us at DPO@schoolpro.uk.
Stay safe and healthy,
The SchoolPro TLC Team
SchoolPro TLC Ltd (2024)
SchoolPro TLC guidance does not constitute legal advice.
SchoolPro TLC is not responsible for the content of external websites.