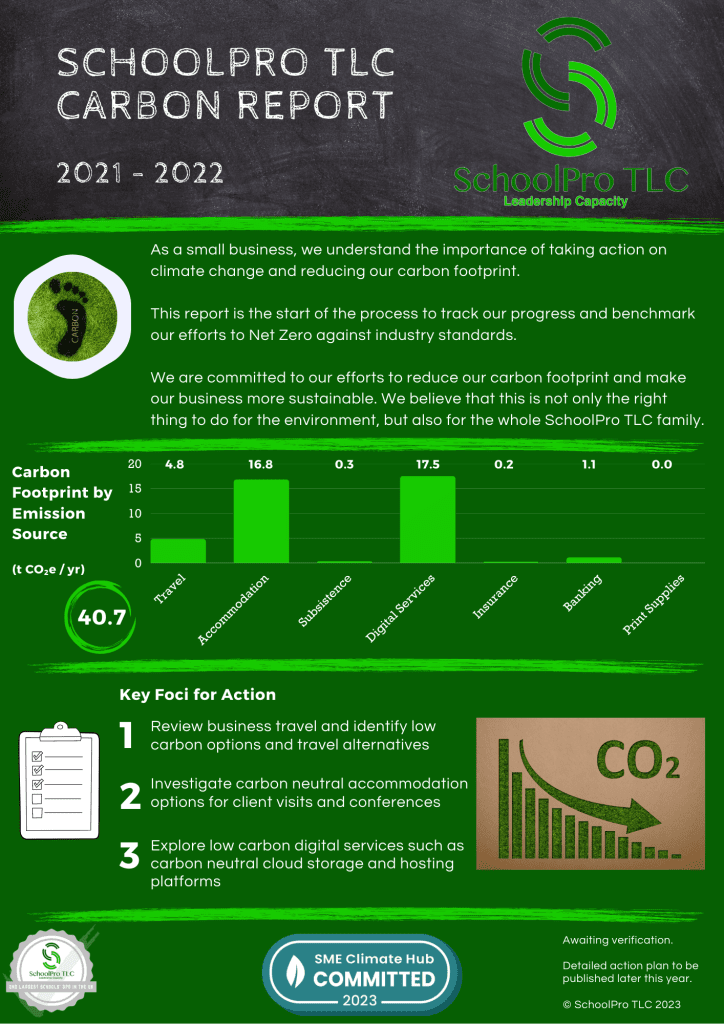
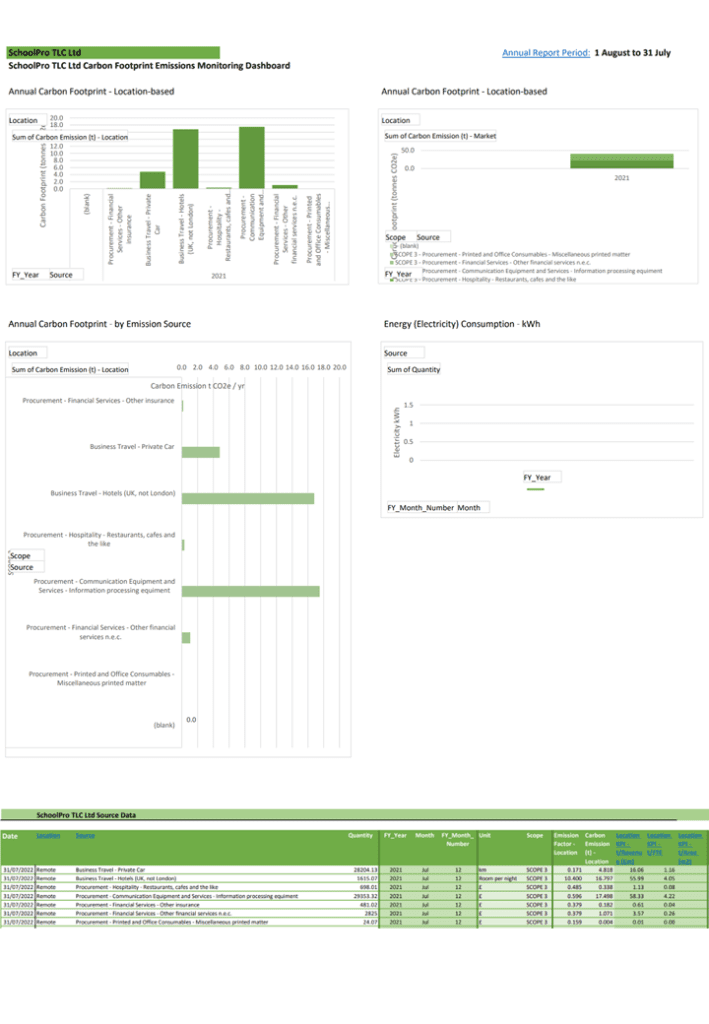
Below is the data from our climate audit that went into producing the report for 2021-22. You can click on the image below to download the audit data and report as a .pdf document.

NGA, NAEE and Derventio Education have come together to provide schools and trusts with a free online tool distributed within SchooliP (the #1 in Teacher Performance Management, CPD & Training and Self Evaluation tools) to help governing boards adopt and develop environmental sustainability as a strategic priority.
If you are a school leader or governor, click here to access the SchooliP Sustainability Portal and register your school for a free account.

Green Careers Week illuminates a vital truth: every profession, including data protection, plays a crucial role in shaping a sustainable future. As we navigate the digital era, the intersection of data protection and environmental stewardship becomes increasingly prominent.
Green Careers Week is not just about celebrating ‘green’ jobs in the traditional sense; it’s about recognising and enhancing the green potential within all career paths. For data protection professionals, this means redefining their role, extending beyond advice on compliance with the UK GDPR to also include fostering eco-friendly practices in data management. This pivotal juncture where data protection meets environmental responsibility marks a new frontier in our journey towards sustainability.
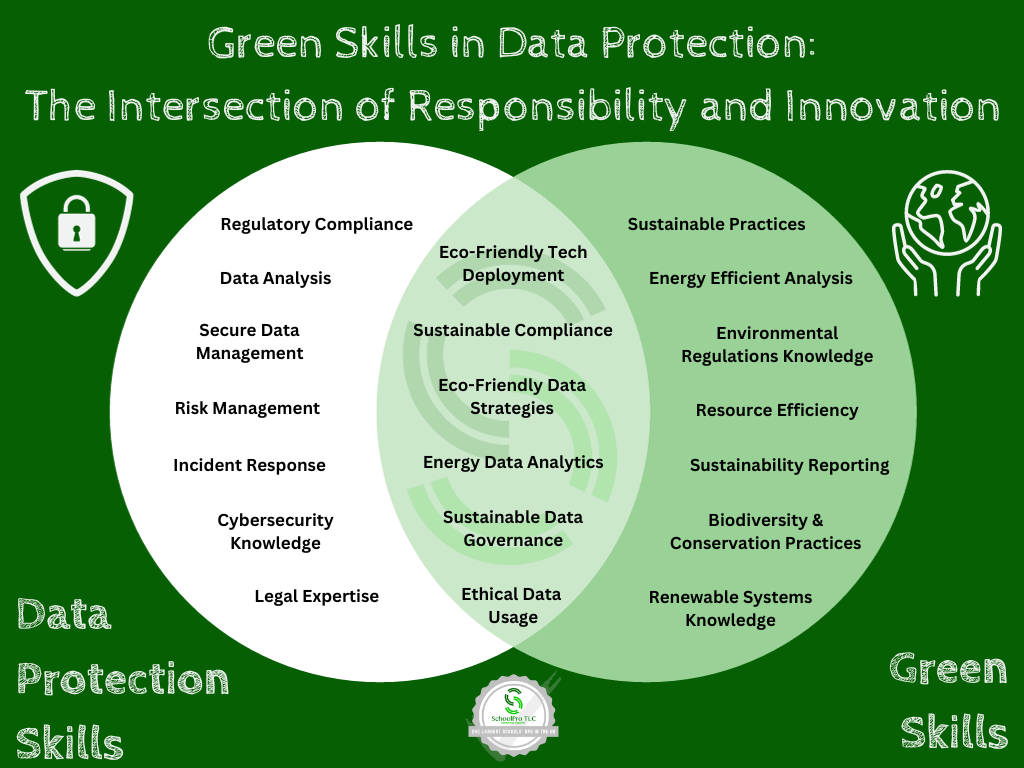
In the evolving landscape of data protection, ‘green skills’ are becoming increasingly vital. These skills blend environmental awareness with technical expertise, equipping professionals to support sustainability initiatives effectively.
Key green skills in data protection include:
🌍 Implementing eco-friendly data storage and processing methods.
🌍 Developing strategies for minimal and sustainable data usage.
🌍 Analyzing energy usage data to identify efficiency improvements.
🌍 Promoting sustainable governance and compliance.
🌍 Understanding and applying regulations that pertain to both data protection and environmental standards.
By mastering these skills, data protection officers can play a pivotal role in driving environmental initiatives within their organizations. Let’s explore ideas around data protection in green careers in more detail:
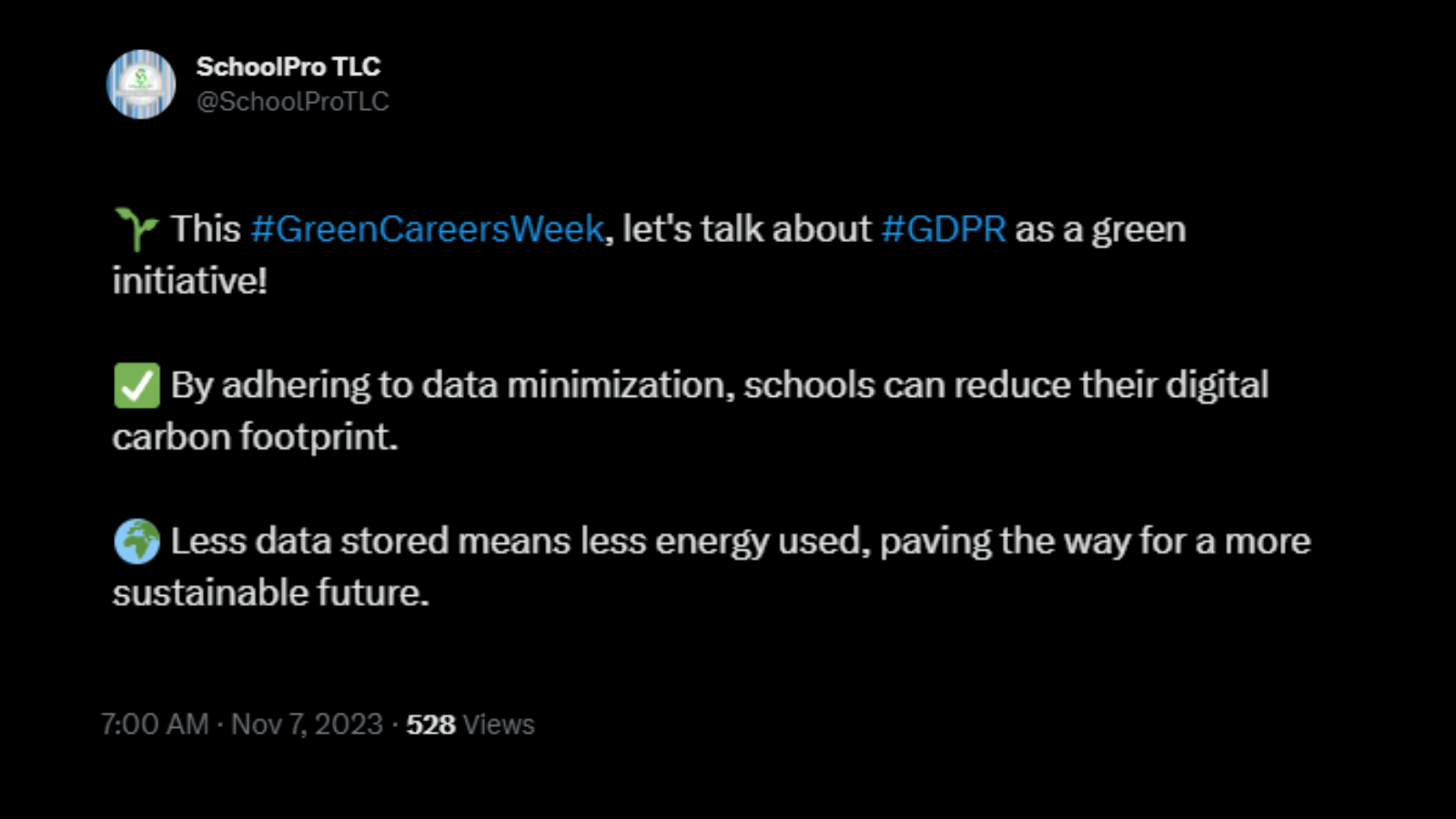
Data protection roles are increasingly recognised as integral to environmental sustainability. This alignment is most evident in the implementation of GDPR’s data minimisation principle. By mandating that personal data collection be “adequate, relevant, and limited to what is necessary,” GDPR inadvertently steers organisations towards greener practices. Less data collected means less storage required, leading to reduced energy consumption in data centres.
This principle not only protects personal data but also encourages a more efficient and environmentally conscious approach to data management. As such, data protection professionals find themselves as key players in reducing the digital carbon footprint, turning data management into an unexpectedly green career path.
The evolution towards energy-efficient data centres and the adoption of cloud computing are pivotal in reducing the environmental impact of digital operations. Data centres, traditionally significant energy consumers, are increasingly transitioning to renewable energy sources and adopting advanced cooling technologies to reduce their carbon footprint.
Cloud computing offers a more energy-efficient alternative to traditional on-premises data centres. With cloud providers optimizing server utilisation and energy use, organisations can significantly lower their environmental impact. Additionally, advancements in data hardware, like the shift from SATA to NVMe and the use of SSDs, enhance performance while consuming less energy, further contributing to sustainability.


Eco-friendly data destruction is an essential component of sustainable data management. Securely disposing of data not only ensures compliance with data protection regulations but also plays a significant role in environmental conservation. Proper methods for data destruction prevent sensitive information from falling into the wrong hands and support the responsible recycling of electronic waste.
This approach minimises the environmental impact of discarded electronic devices, which are a major source of pollution and resource depletion. By integrating eco-friendly data destruction practices, organisations can protect both their data and the environment.
The digital transformation in schools significantly contributes to reducing paper usage, offering dual benefits in data protection and environmental sustainability. Shifting from paper-based to digital records not only minimises the risk of physical data breaches but also reduces paper waste, directly impacting environmental conservation.
This transition towards digital documentation aligns with sustainable practices, fostering a culture of eco-consciousness in educational settings. By embracing digital methods, schools can efficiently manage data while actively participating in environmental stewardship.

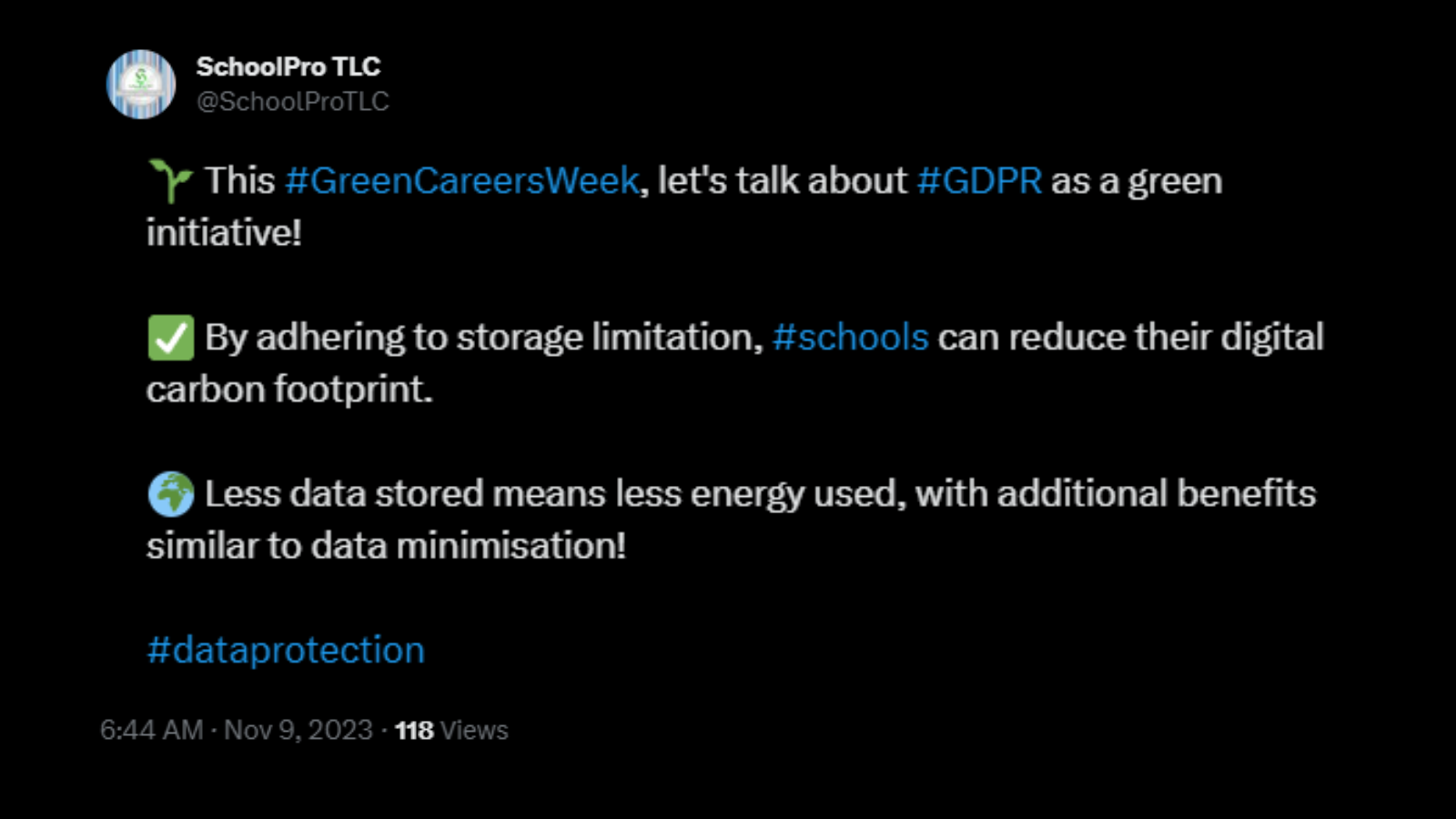
Another useful tool in reducing the energy costs of data storage and processing is the Storage Limitation Principle of the UK GDPR. This principle calls for data to be kept “for no longer than is necessary for the purposes for which the personal data are processed,” encouraging businesses to retain data in an identifiable form for as short a time as necessary.
Much like the Data Minimisation Principle, this approach not only cuts costs but also reduces energy usage by eliminating unnecessary data storage and processing.
By embracing green practices within data protection roles, we can not only safeguard sensitive information but also contribute to a sustainable future. By integrating principles like UK GDPR’s data minimisation and storage limitation, adopting energy-efficient data centres and cloud computing, practicing eco-friendly data destruction, and reducing paper use, data protection becomes a vital ally in environmental stewardship.
Let’s work to merge data protection with sustainability, forging a path where technological advancement and ecological responsibility coexist.
The SME Climate Hub is an initiative of the We Mean Business Coalition, the Exponential Roadmap Initiative, the United Nations Race to Zero campaign and the International Chamber of Commerce. In collaboration with Normative and the Net Zero team at Oxford University, the SME Climate Hub provides tools and resources to enable SMEs to make a climate commitment, take action and measure their progress. This partnership is an exercise in radical collaboration that opens the doors for SMEs to join the United Nations Race to Zero campaign — an international campaign that brings together an unprecedented coalition of real economy actors and 120 governments committed to achieve net-zero emissions by no later than 2050.

The SME Climate Hub provides small and medium sized businesses with a one-stop-shop to make a climate commitment and access best-in-class tools and resources to mitigate their environmental impact and build resilient businesses for the future.
The SME Climate Hub was founded by the We Mean Business Coalition, Exponential Roadmap Initiative, the International Chamber of Commerce, and the United Nations Race to Zero campaign in collaboration with Oxford University and Normative. This partnership is an exercise in radical collaboration that allows SMEs to join the United Nations Race to Zero, an international campaign that brings together an unprecedented coalition of real economy actors and 120 governments committed to achieving net-zero emissions by no later than 2050.
Over 2,600 SMEs across 84 different countries have made the commitment, with key sectors including retail, energy, manufacturing, agriculture, technology. Learn more at: www.smeclimatehub.org



Small to medium sized enterprises account for 90% of business worldwide and affect the livelihoods of over 2 billion people. However, in the global effort to mitigate climate change, large businesses and governments have largely been the focus of the discussion. The SME Climate Hub aims to bring all businesses on board to net zero.
The SME Climate Hub mobilizes and supports small and medium sized businesses to commit to cut carbon emissions in half by 2030 and reach net zero emissions before 2050 — a milestone aimed at avoiding the worst effects of climate change while ensuring business viability.

Business Resilience
By taking climate action through the SME Climate Hub, small businesses can better navigate the shifting expectations of consumers, large corporations, and governments.
Climate action gives SMEs a competitive advantage and enables them to future-proof their business by:
Supply Chain Resilience
Large corporations from every industry and region of the world are setting net-zero goals to align with science and build business resilience. To meet these goals, multinational corporations are accelerating decarbonization demands for SMEs in their global supply chains and steering their procurement process towards climate action in suppliers.
Small businesses often lack the resources needed to decarbonize. Multinational companies, governments, and tools such as those provided by the SME Climate Hub need to bridge the gap, to ensure no one is left behind in the transition to net zero.
Several major multinational corporations, including Ericsson, IKEA, Telia, BT Group and Unilever, Nestlé and Tech Mahindra, have set targets to reach net-zero emissions in their value chains, and they have committed to supporting the SME Climate Hub through the 1.5°C Supply Chain Leaders, a group of multinational corporations accelerating climate action throughout their global supply chains.
Community
Joining the SME Climate Hub allows small businesses to join a community of like minded companies prioritizing climate action. Committed companies can position themselves at the forefront of their industries, alongside other leading players.
International recognition
The SME Climate Commitment is the official pathway for small and medium sized businesses to join the Race to Zero. Businesses which commit to the SME Climate Hub will be globally recognized by the United Nations’ Race to Zero campaign.




The SME Climate Hub calls on small and medium sized businesses from around the world to join the commitment, and on national governments to take ambitious steps to build local SME climate action.
The science is clear: we need to halve our emissions by 2030 to deliver a zero-carbon world in time. To meet this goal, every business, no matter their size or industry, has a role to play. We need all companies around the world to commit to a net-zero future.


















For a confidential conversation about the needs of your school or organisation, please contact SchoolPro TLC using the links below. Based in Gloucestershire, available anywhere in the UK!
SchoolPro TLC Limited was formed by school and education leaders with over 60 years of experience across all stages of education and in a variety of contexts. The company founders have worked to improve educational provision as both senior leaders and school governors.
Monday – Friday : 8am – 6pm
SchoolPro TLC Ltd
Unit 1b Aerotech Business Park, Bamfurlong Lane, Cheltenham, United Kingdom, GL51 6TU
© 2025 SchoolPro TLC – All Rights Reserved